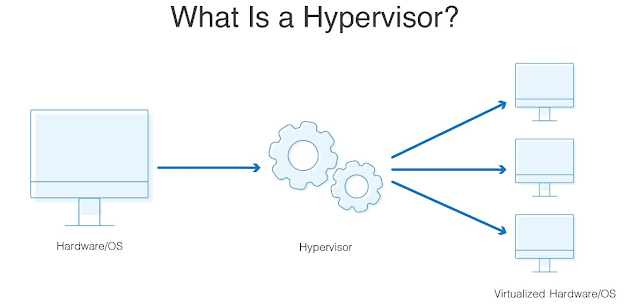
Hypervisors: The Key to Efficient Resource Utilization and Virtualization
Hypervisors provide a wide range of benefits, including:
- Resource
Utilization: Hypervisors allow multiple virtual machines to share the
physical resources of a single machine, such as CPU, memory, and storage.
This can lead to greater overall utilization of the physical resources and
reduced costs.
- Isolation:
Each virtual machine operates independently of the others, with its own
virtualized hardware resources. This isolation provides improved security
and reduces the risk of one virtual machine impacting the others on the
same physical machine.
- Flexibility:
Virtual machines can be created, started, stopped, and moved between
physical machines easily, providing a high level of flexibility in
deploying and managing computing resources.
- Testing
and Development: Hypervisors enables developers and testers to create and
test new software and configurations in virtual environments, without
impacting production systems or requiring dedicated physical hardware.
- High
Availability: Hypervisors provide features such as live migration, which
allow virtual machines to be moved between physical machines without
downtime, enabling high availability and fault tolerance.
- Disaster
Recovery: Virtual machines can be replicated to remote physical machines
or cloud environments, providing a fast and efficient way to recover from
disasters or other disruptions.
Understanding
the Different Types of Hypervisors and the Differences between them.
There are two main types of hypervisors, which are commonly
referred to as Type 1 hypervisors and Type 2 hypervisors. Let's take a closer
look at each type and the differences between them:
Type 1
Hypervisors:
Type 1 hypervisors, also known as bare-metal hypervisors, are
installed directly on the host machine's physical hardware. This type of
hypervisor has direct access to the hardware resources, allowing it to control
and allocate resources to the virtual machines. Type 1 hypervisors are
typically used in enterprise data centers and cloud computing environments.
Examples of Type 1 hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V Server,
and Citrix Hypervisor.
Advantages
of Type 1 Hypervisors
- High
Performance: Type 1 hypervisors have direct access to the physical
hardware resources, allowing them to provide better performance compared
to Type 2 hypervisors.
- Improved
Security: Type 1 hypervisors provide better security compared to Type 2
hypervisors as they have direct access to the hardware and can isolate
virtual machines from each other.
- Scalability:
Type 1 hypervisors can scale better compared to Type 2 hypervisors due to
their direct access to the physical hardware resources.
- Flexibility:
Type 1 hypervisors are highly flexible and can be used in a wide range of
enterprise environments, from data centers to cloud computing.
Disadvantages
of Type 1 Hypervisors
- Complexity:
Type 1 hypervisors are more complex to set up and manage compared to Type
2 hypervisors.
- Cost:
Type 1 hypervisors are often more expensive compared to Type 2 hypervisors
due to their higher performance and additional features.
Type 2
Hypervisors
Type 2 hypervisors, also known as hosted hypervisors, are
installed on top of an existing operating system. This type of hypervisor
relies on the underlying operating system to provide access to the hardware
resources. Type 2 hypervisors are commonly used on desktop or laptop computers
for virtualization, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single
physical machine. Examples of Type 2 hypervisors include Oracle VirtualBox,
VMware Workstation, and Parallels Desktop.
Advantages
of Type 2 Hypervisors
- Ease of
Use: Type 2 hypervisors are easier to set up and use compared to Type 1
hypervisors, as they rely on an existing operating system.
- Lower
Cost: Type 2 hypervisors are often less expensive compared to Type 1 hypervisors,
making them a good choice for individual users or small businesses.
- Compatibility:
Type 2 hypervisors can run on a wide range of hardware platforms, making
them highly compatible.
Disadvantages
of Type 2 Hypervisors
- Performance:
Type 2 hypervisors have lower performance compared to Type 1 hypervisors
due to their reliance on the underlying operating system.
- Security:
Type 2 hypervisors provide less security compared to Type 1 hypervisors as
they rely on the underlying operating system for security.
- Scalability:
Type 2 hypervisors have limited scalability compared to Type 1 hypervisors
due to their reliance on the underlying operating system.
Differences between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisors
The main differences between Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors are as
follows:
- Architecture:
Type 1 hypervisors are installed directly on the physical hardware of the
host machine, while Type 2 hypervisors are installed on top of an existing
operating system.
- Resource
Allocation: Type 1 hypervisors have direct access to the physical hardware
resources, allowing them to allocate resources to virtual machines with
greater efficiency and performance than Type 2 hypervisors.
- Complexity:
Type 1 hypervisors are typically more complex to configure and manage than
Type 2 hypervisors, as they require direct access to the physical hardware
resources.
- Performance:
Type 1 hypervisors generally offer better performance than Type 2
hypervisors, as they have direct access to the physical hardware
resources.
Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice
of which type to use will depend on the specific needs of the organization or
individual.



Comments
Post a Comment